The easiest way to deploy Simplicity smart contracts on Liquid testnet using the Web IDE. (Guide Not directly affiliated with Blockstream or Simplicity-Lang)
Developer Documentation -SimplicityHL Rust Docs -SimplicityHL Repo -SimplicityHL Code Examples
Simplicity is a low-level, formally verifiable programming language designed specifically for blockchain smart contracts. Unlike traditional smart contract languages, Simplicity prioritizes:
- Formal Verification: Programs can be mathematically proven to be correct
- Static Analysis: Resource usage (CPU, memory) is known before execution
- Security: Minimal attack surface with clear, auditable semantics
- Efficiency: Optimized for blockchain validation
Current Status:
- Liquid Network: Simplicity is currently active on Liquid testnet and will soon be available on Liquid mainnet
- Bitcoin: Simplicity is compatible with Bitcoin but requires a soft fork activation (future)
Architecture:
- Simplicity programs are deployed as Taproot script paths (P2TR)
- Programs execute in a bit machine (not stack-based)
- Uses jets (optimized opcodes) for common operations like signature verification
- Compatible with BIP-340 Schnorr signatures and BIP-341 Taproot
SimplicityHL is the high-level language that compiles to Simplicity, similar to how Rust compiles to assembly language.
- Write: Developer writes a contract in SimplicityHL (
.simffile) - Compile: SimplicityHL compiler (
simc) converts it to Simplicity bytecode- Implementation:
SimplicityHL/src/compile.rs- translates SimplicityHL AST to Simplicity combinators
- Implementation:
- Commit: The program's CMR (Commitment Merkle Root) is computed
- Implementation:
rust-simplicity/src/merkle/cmr.rs- Merkle root that commits to program structure
- Implementation:
- Address: A P2TR address is derived from the CMR
- Fund: Bitcoin/Liquid is sent to the address
- Spend: To spend, you provide:
- The Simplicity program
- Witness data (signatures, hash preimages, etc.)
- The transaction spends the UTXO if the program evaluates to
true
Execution Model:
Transaction → Simplicity VM → Program + Witness → Evaluate → Accept/Reject
The program has access to transaction data (sighash) through jets like jet::sig_all_hash().
Technical Details:
- Jets: Optimized native implementations of common operations. For example,
jet::bip_0340_verifyis implemented inrust-simplicity/simplicity-sys/depend/simplicity/jets-secp256k1.c(C) with Rust bindings - Sighash: Computed in
rust-simplicity/src/policy/sighash.rsusingElementsEnv::c_tx_env().sighash_all() - Transaction Environment: Elements-specific environment built in
rust-simplicity/simplicity-sys/depend/simplicity/elements/txEnv.c
This is the easiest way to get started with Simplicity on testnet! No installation required, works in your browser.
https://ide.simplicity-lang.org
Advantages:
- No installation required (browser-based)
- Automatic sighash computation
- Built-in key management
- Visual transaction builder
- Automatic witness encoding
- Direct broadcast to testnet
- Real-time error checking
Constants:
- Testnet Blockhash: a771da8e52ee6ad581ed1e9a99825e5b3b7992225534eaa2ae23244fe26ab1c1
- Internal Key: 0xf5919fa64ce45f8306849072b26c1bfdd2937e6b81774796ff372bd1eb5362d2
Source: https://github.com/BlockstreamResearch/simplicity-webide
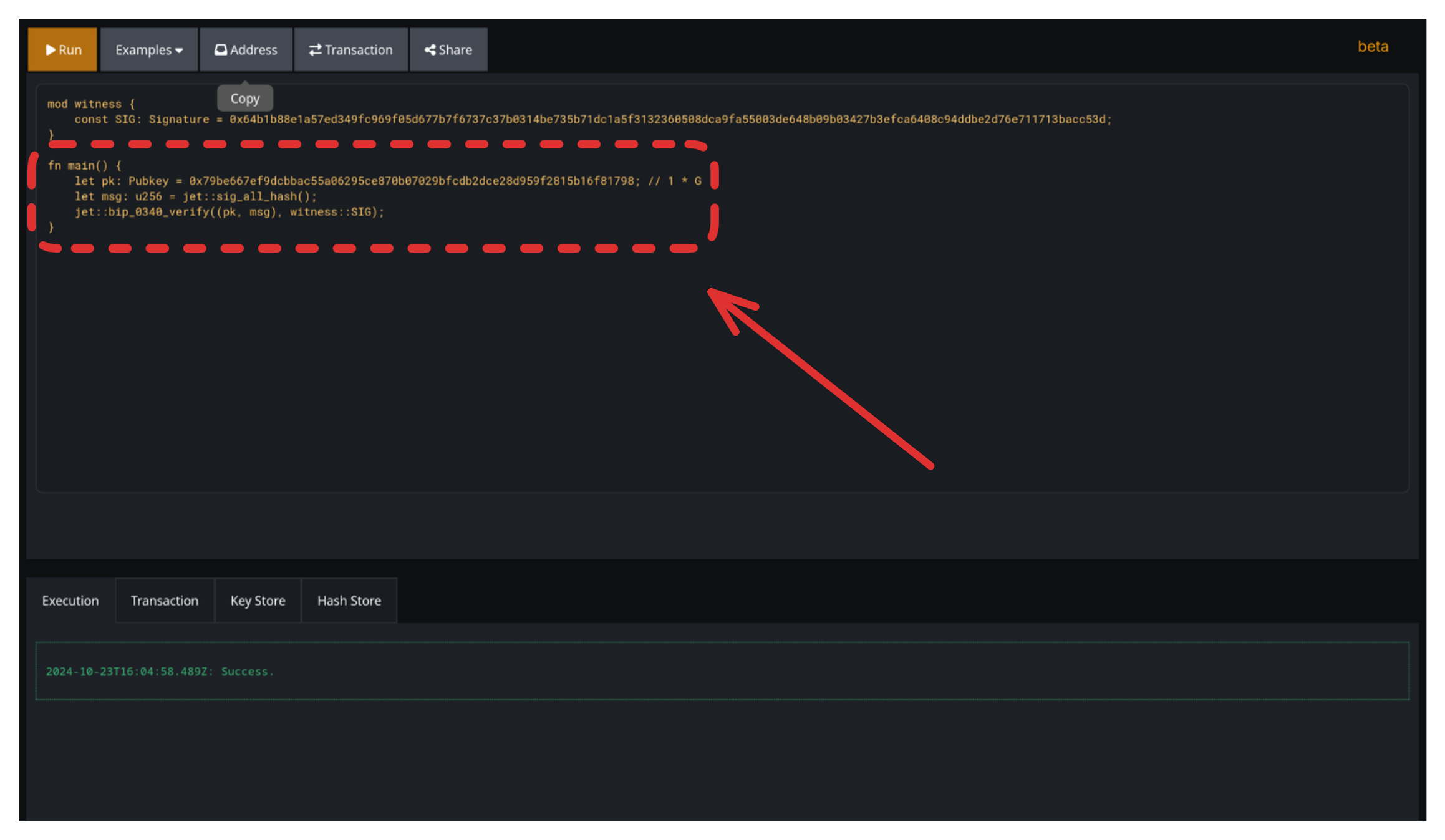
Open https://ide.simplicity-lang.org in your browser. You'll see a default P2PK contract.
You can customize it or use example contracts like:
Simple contract
fn main() {
()
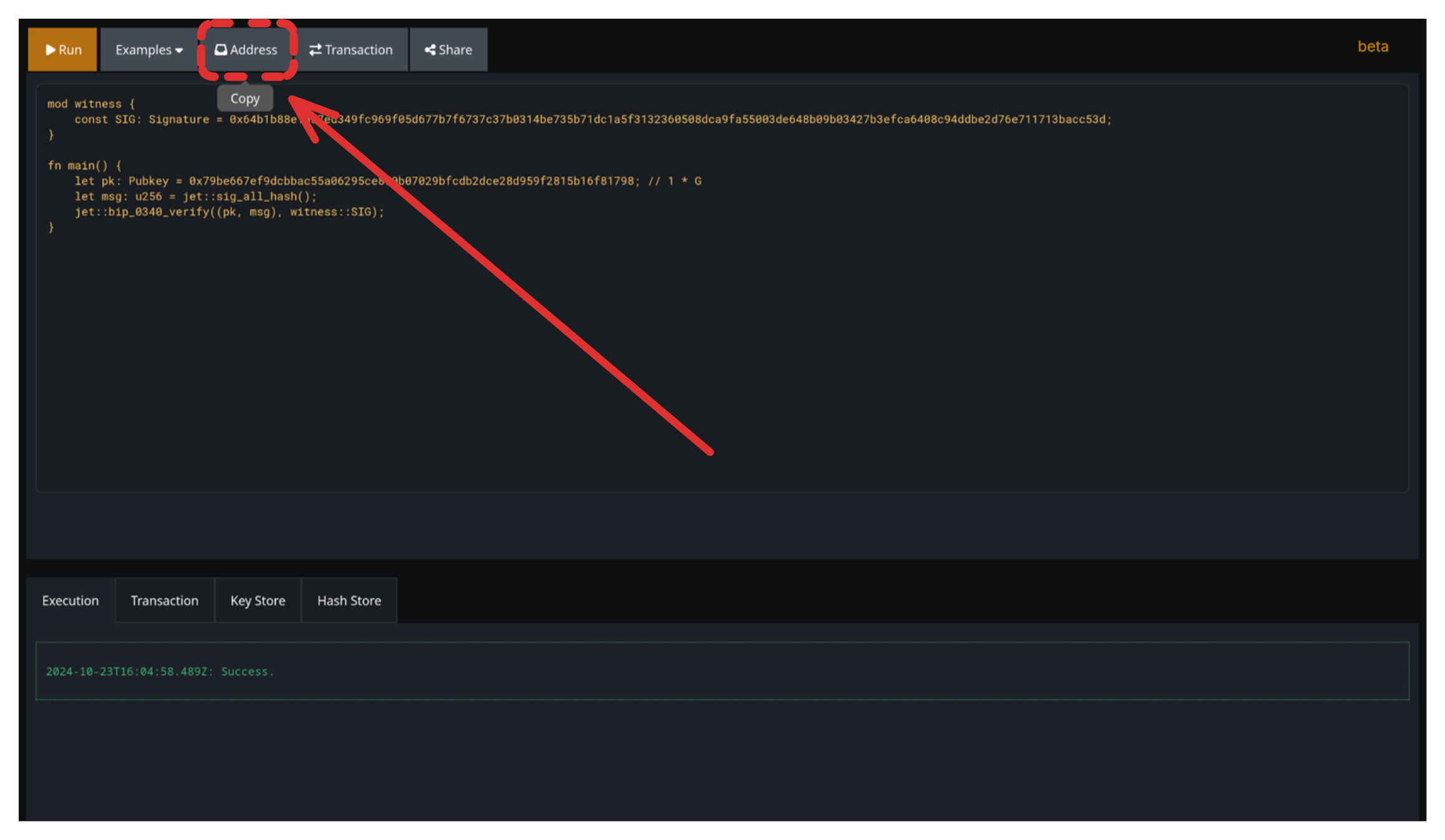
}Click the "Address" button. The address is copied to your clipboard.
Keep the Web IDE tab open!
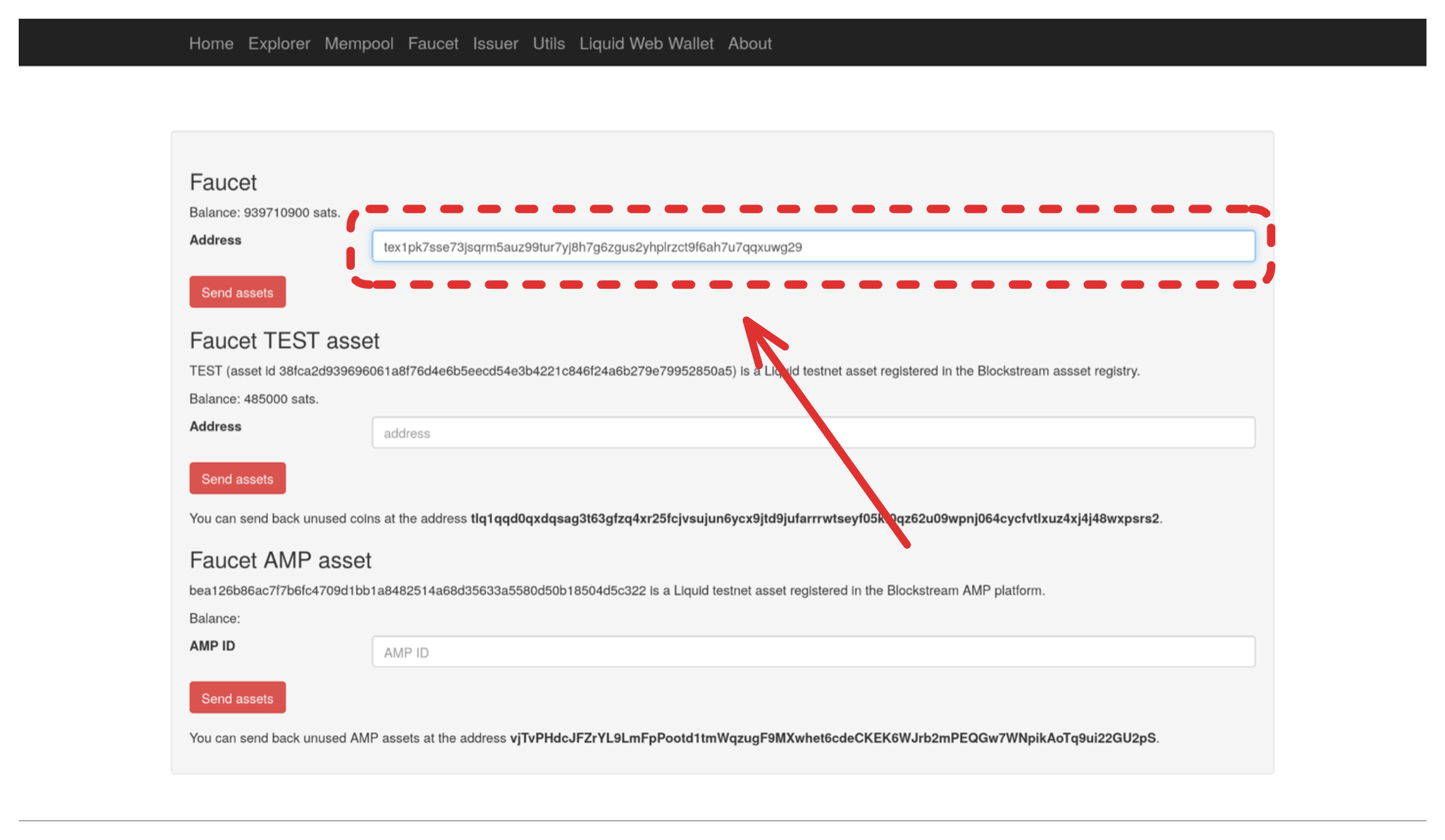
- Go to https://liquidtestnet.com/faucet
- Paste your address
- Click "Send assets"
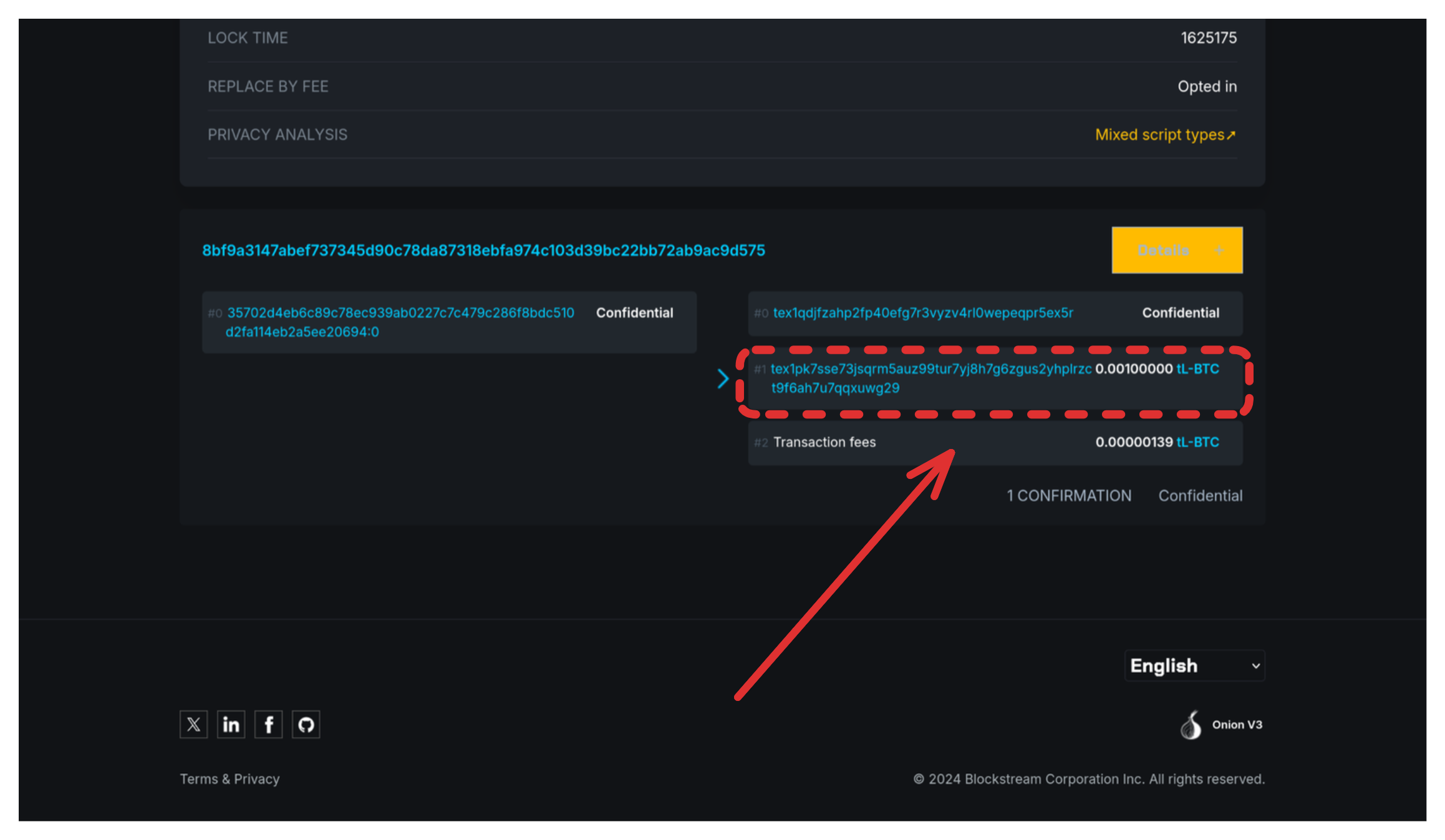
- Copy the transaction ID
- Go to https://blockstream.info/liquidtestnet
- Paste the transaction ID
- Wait for confirmation (~1 minute)
- Note the vout and value (usually vout=1, value=100000)
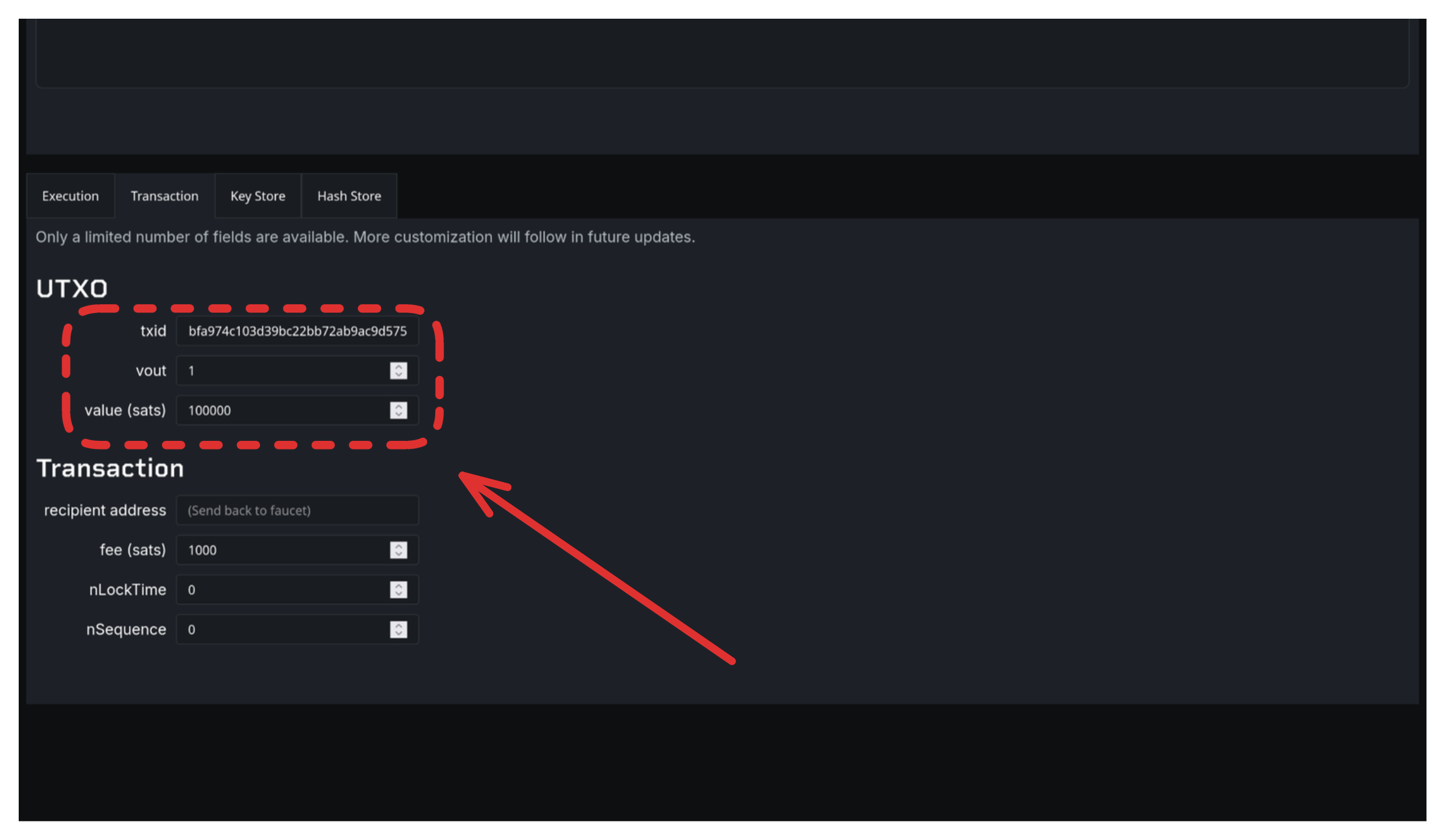
Go back to the Web IDE, scroll to "Transaction" section:
- Txid: Paste funding transaction ID
- Vout: Enter output index (e.g.,
1) - Value: Enter amount (e.g.,
100000)
Leave other fields as defaults.
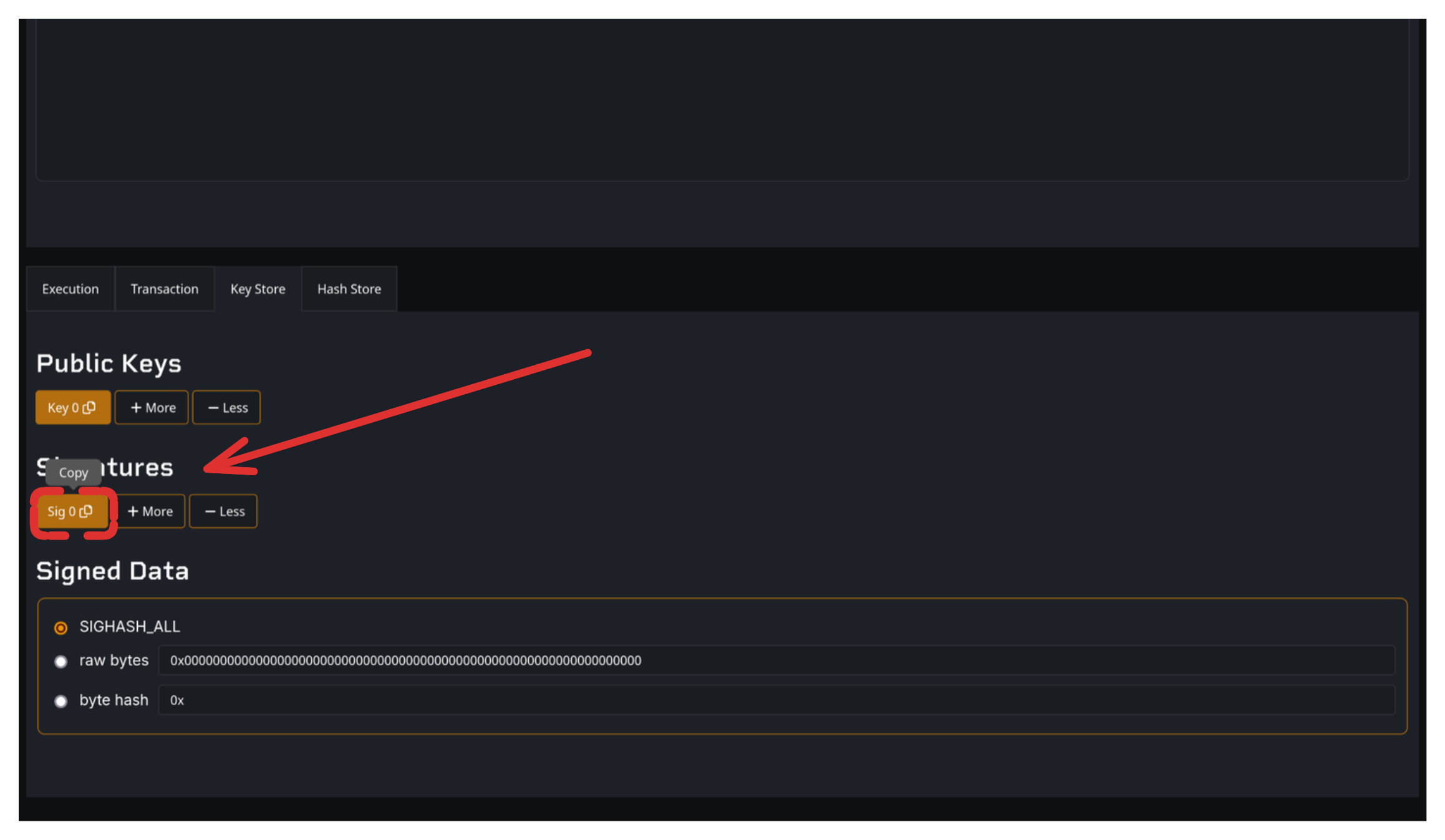
For contracts with signatures (like P2PK):
- Click "Sig 0" button
- Signature is copied to clipboard
- Paste into your witness section
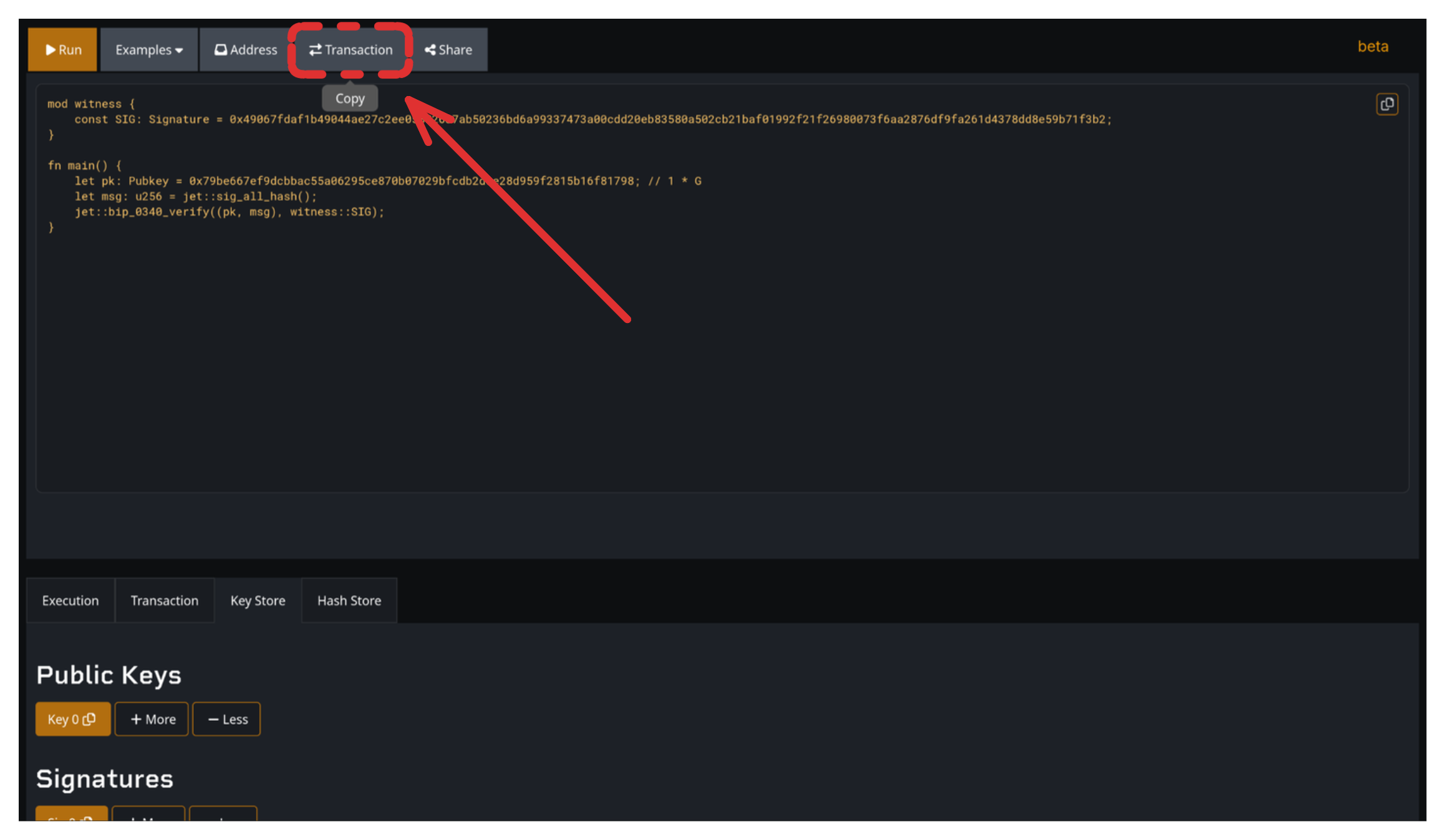
Update your code:
mod witness {
const SIGNATURE: Signature = 0xf74b3ca574647f8595624b129324afa2...;
}Click the "Transaction" button. The complete transaction hex is copied to clipboard.
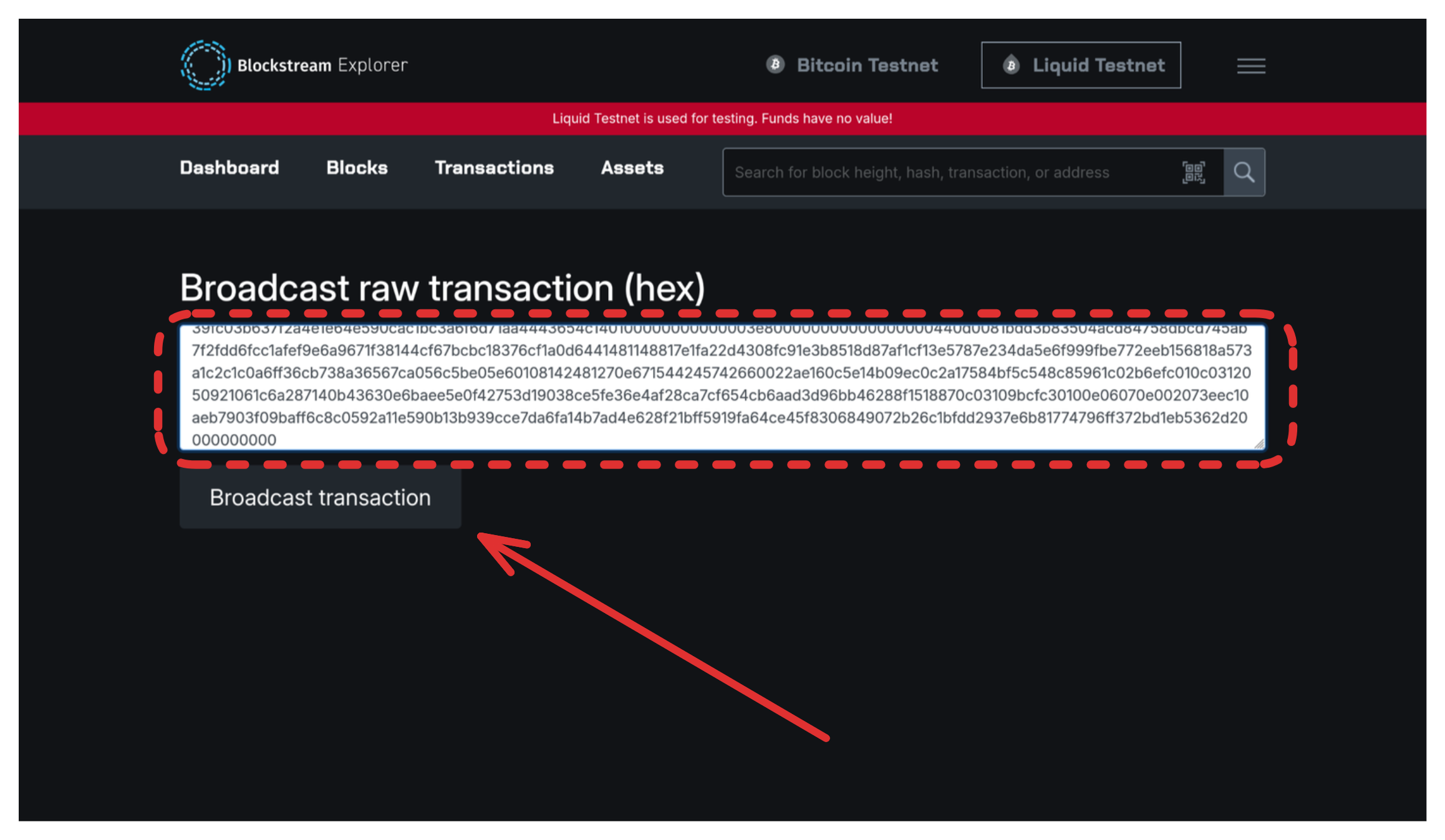
- Go to https://blockstream.info/liquidtestnet/tx/push
- Paste transaction hex
- Click "Broadcast transaction"
Success! View your transaction on the explorer.
For advanced users who want command-line control and access to the hal-simplicity, see:
CLI_GUIDE.md - Complete command-line deployment guide (Work in Progress)
Explore more advanced contract examples:
SimplicityHL Examples Repository:
https://github.com/BlockstreamResearch/SimplicityHL/tree/master/examples
Example Contracts:
- p2pk.simf - Pay to public key (code)
- p2pkh.simf - Pay to public key hash (code)
- p2ms.simf - Pay to multisig (code)
- htlc.simf - Hash Time-Locked Contract (code)
- hodl_vault.simf - Time-locked vault (code)
- ctv.simf - CheckTemplateVerify covenant (code)
- escrow_with_delay.simf - Escrow with timeout (code)
- last_will.simf - Inheritance contract (code)
- sighash_all_anyonecanpay.simf - Custom sighash modes (code)
- non_interactive_fee_bump.simf - Fee bumping without cooperation (code)
Study the Code:
Each example includes corresponding .wit (witness) files showing how to provide the required witness data. The examples demonstrate practical patterns you can adapt for your own contracts.
Simplicity Web IDE:
https://ide.simplicity-lang.org
- Visual contract development
- Built-in sighash computation
- Transaction builder
- Live on-chain deployment
Important: Simplicity is a stateless contracting system. Each contract execution is independent and doesn't maintain persistent state between transactions. This is by design for security and formal verification.
Despite being stateless, Simplicity enables powerful and interesting use cases:
1. Advanced Payment Conditions
- Multisignature: M-of-N signature requirements
- Timelocks: Absolute or relative time/height locks
- Hash Time-Locked Contracts (HTLCs): Lightning Network-style contracts
- Covenant Restrictions: Control where funds can be sent
2. Vaults and Security
- Delayed Withdrawals: Require waiting period for large withdrawals
- Emergency Recovery: Backup keys that activate after timelock
- Decaying Security: Multisig that reduces signatures needed over time
3. Inheritance and Estate Planning
- Time-Locked Inheritance: Funds unlock to heirs after inactivity period
- Multi-Beneficiary Distribution: Split funds between multiple heirs
- Conditional Release: Release funds based on multiple criteria
4. Atomic Swaps
- Cross-Asset Swaps: Trustless swaps between different assets on Liquid
- Cross-Chain Swaps: Atomic swaps with other UTXO chains
- Hash-Locked Contracts: Trustless exchange using hash preimages
5. Oracle Integration
- Signature Verification: Verify signed data from trusted oracles
- Price-Based Conditions: Execute only if price is within bounds
- Time-Stamped Data: Verify oracle data with timestamps
6. Covenant Applications
- Spending Restrictions: Limit where and how funds can move
- Output Templates: Enforce specific output patterns (similar to CTV)
- Fee Bumping: Non-interactive transaction fee increases
STARK Proof Verification: With OP_STARKVERIFY integration, Simplicity contracts can verify zero-knowledge proofs, enabling verification of off-chain computation and potentially bridging to other systems.
Payment Channels: Custom payment channel logic with more flexible conditions than standard Lightning.
Complex Multisig: Signature requirements that change based on amount, destination, or time.
While stateless, Simplicity's formal verification capabilities and expressive power enable creating highly secure, auditable smart contracts for specific use cases. As the ecosystem develops, we expect to see interesting combinations of Simplicity contracts with off-chain computation and layer 2 systems.
- GitHub Issues: Report bugs or request features
- SimplicityHL: https://github.com/BlockstreamResearch/SimplicityHL/issues
- hal-simplicity: https://github.com/apoelstra/hal/issues
- Fork a core repository Blockstream Research
- Improve existing docs
- Write tutorials and guides
- Create example contracts
- Translate documentation
- Twitter: Follow @SimplicityLang for updates and discussions
- Telegram: Join the Simplicity Telegram group to connect with developers
- Better error messages
- Debugging tools
- Testing frameworks
This guide is released under CC0-1.0 (Public Domain).